Proportionality
There are direct and inverse proportionality.
Direct proportionality
Example: Flour costs 10 ¤, and bread 20 ¤. If we raise the price of flour, then the price of bread will also increase, as its cost will rise.Such a dependence is called direct proportionality.
Inverse proportionality
Example: A liter of milk cost 30 ¤, and for 60 ¤ we could buy 2 liters of milk, but then the price of milk dropped to 20 ¤ per liter, meaning for the same 60 ¤ we can already buy 3 liters of milk, resulting in a dependence: the price went down, and the number of liters for the same amount increased, such a dependence is called inverse proportionality.Solving proportions
Rule: The product of the extreme terms equals the product of the middle terms, this rule is also called the rule of «cross».Proportion can be solved in two ways. According to the formulas of proportionality:
1st method
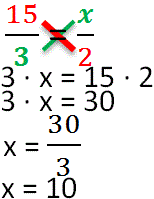
2nd method
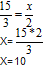
The second method is much simpler and more convenient than the first.
