Calculation of the friction hydraulic resistance coefficient of pipes
As known, hydraulic resistance depends on several factors, one of which is friction. It arises as a result of the contact of the medium being pumped through the pipe and its internal surface, which usually has roughness and irregularities. This contact causes a kind of friction, which as a result causes a braking effect. Therefore, it is necessary to calculate the losses associated with friction. This can be calculated using a calculator or by performing a manual calculation using a formula.
| Liquid flow rate | ||
|
Kinematic viscosity coefficient ( for water at temp. 100C = 1,3, 200C = 1) |
||
| Pipe diameter | ||
| Pipe length | ||
| Liquid density | ||
| Wall roughness coefficient of the pipeline | ||
|
| ||
| Flow regime | ||
| Liquid flow speed in the pipeline, m/c | ||
| Reynolds number (Re) | ||
| Friction coefficient (λ) | ||
| Hydraulic resistance coefficient (ξ) | ||
| Pressure loss (Δp), Pa | ||
For independent use, the following formula is used:
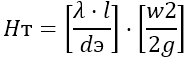
Ht – loss;
[w2/(2g)] – velocity head;
λ – friction coefficient;
l – pipe length;
de – equivalent diameter;
w – speed;
g – acceleration of fall.
