Rhombus Diagonals
A rhombus is a quadrilateral that is a parallelogram, retains all its properties, but in addition, it is equilateral. Since all sides of the rhombus are equal, and from the properties of a parallelogram its opposite angles are also equal to each other, the diagonals of the rhombus not only intersect at a point dividing them into two equal parts each, but they will always be perpendicular to each other.
When diagonals are drawn in a rhombus, they divide it into four congruent right triangles, whose legs are halves of the diagonals. In any of the resulting right triangles, knowing the hypotenuse (side of the rhombus), calculate both legs. For these purposes, trigonometric ratios of sine and cosine in the right triangle are used - since both legs, we temporarily assume them to be a and b, unknown, for calculations one of the acute angles in the triangle will be needed.
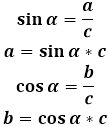
To convert these formulas into the parameters of the rhombus, it is necessary to relate the sides of the triangle to the sides and diagonals of the rhombus, as well as the acute angle of the triangle with the angles of the rhombus.
The side of the rhombus, as agreed, becomes the hypotenuse of the triangle, and the halves of the diagonals take on the role of legs. Then in reverse order, to find the full diagonals, each calculated leg will need to be doubled.
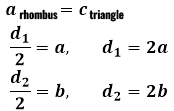
The angle used in the sine and cosine for finding the legs and then the diagonals of the rhombus is nothing but half the angle of the rhombus itself since the diagonals of the rhombus are the bisectors of its angles. Therefore, the following equality will be true:
Or
αrhombus/2=αtriangle
Now to derive the general formula for the diagonals of the rhombus through the side of the rhombus and its angle (by the way, the choice of the acute or obtuse angle does not affect the calculation results) the written replacements must be substituted into the original triangle formulas from which the calculation algorithm began.
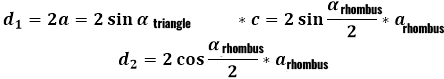
After performing the calculations in reverse, you can also find the side of the rhombus through the diagonals or the angle between the sides of the rhombus.
